Data Science
Data Science is an interdisciplinary field about scientific methods, processes and systems to extract knowledge or insights from data in various forms, either structured or unstructured.
Data Science employs techniques and theories drawn from many fields within the broad areas of mathematics, statistics, information science, and computer science, in particular from the subdomains of machine learning, classification, cluster analysis, data mining, databases, and visualization.
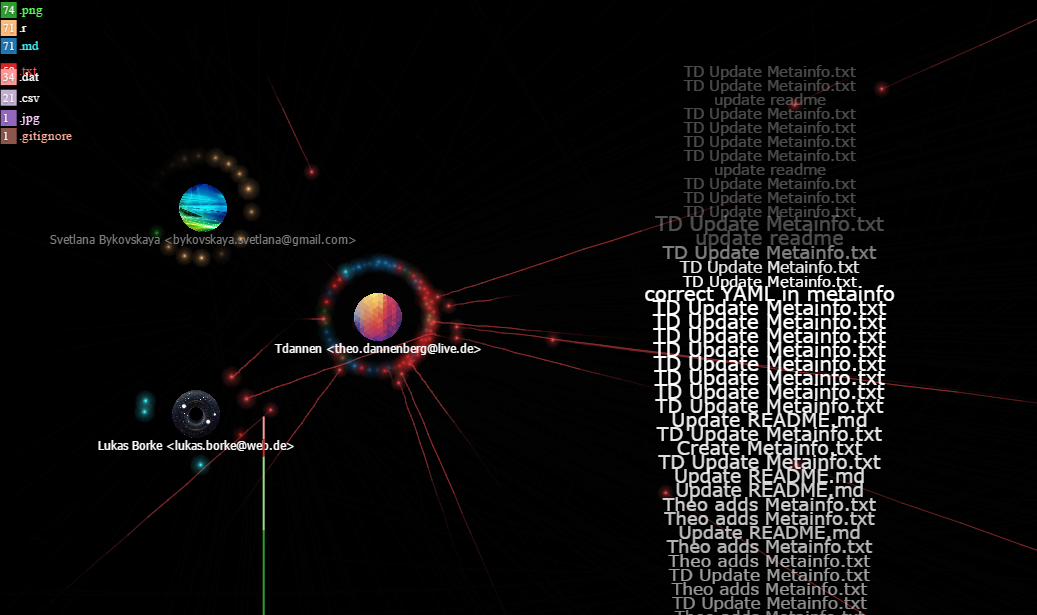
Collaboration Timeline of the GitHub repository via GitHub Visualizer
Data mining is the computational process of discovering patterns in large data sets involving methods at the intersection of artificial intelligence, machine learning, statistics, and database systems. The overall goal of the data mining process is to extract information from a data set and transform it into an understandable structure for further use.
Big Data
The result of an extensive literature review on Big Data definitions by De Mauro et al. (2015) concluded that a consensual definition of Big Data would be that “Big Data represents the Information assets characterized by such a High Volume, Velocity and Variety to require specific Technology and Analytical Methods for its transformation into Value”.
The current Wikipedia definition describes Big Data by the following characteristics:
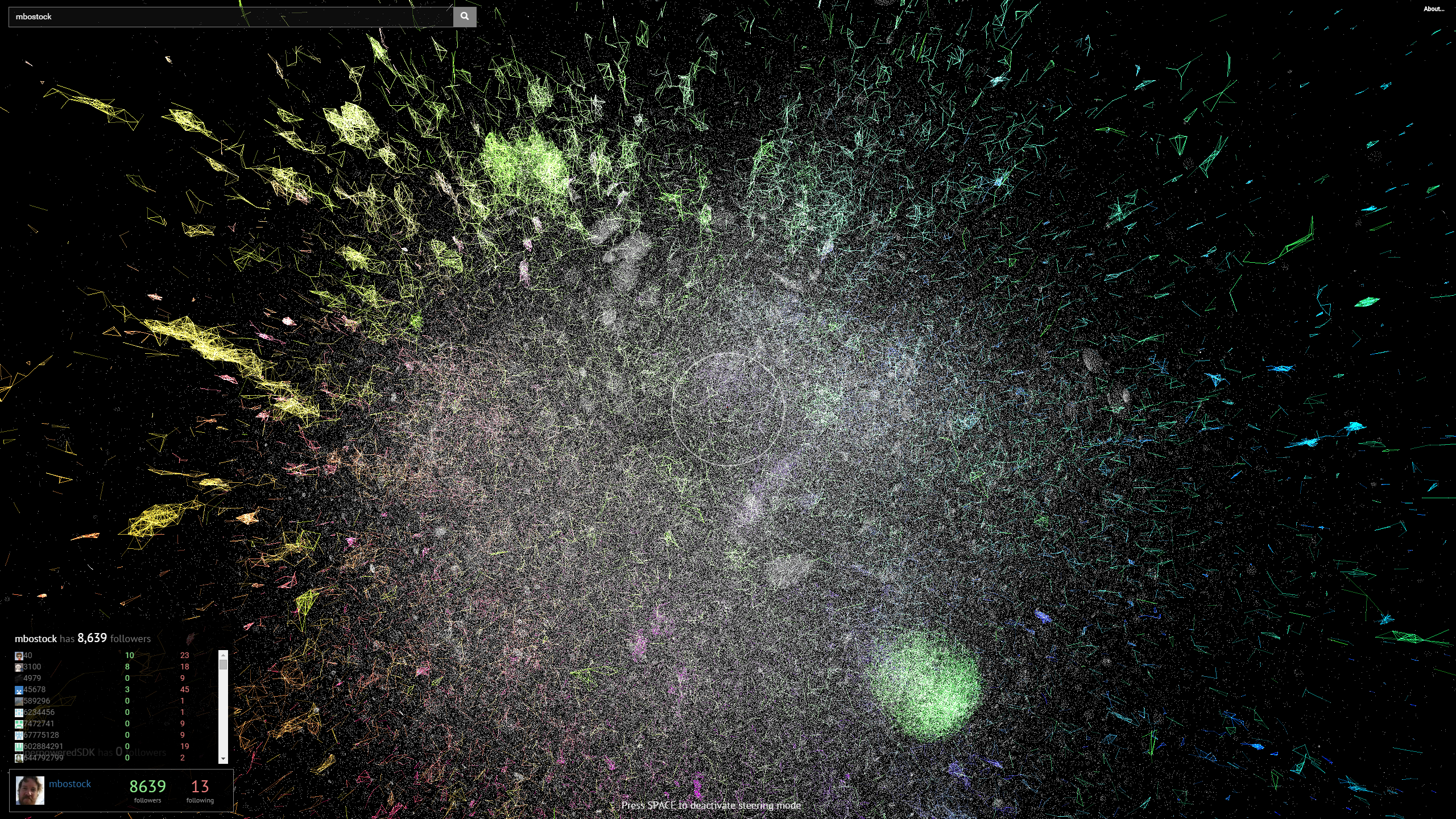
Software Galaxies: 3D GitHub followers visualization
Smart Data
The Smart Data Memorandum, which is an initiative of the Trusted Cloud research, discussed the specifications and definitions of the term "Smart Data" regarding the delimitation of the term "Big Data" and established the concise formula:
Smart Data = Big Data + Value + Semantics + Data quality + Security + Data protection
= useful, high-quality and secured/verified Data
According to the Smart Data experts from trommsdorff + drüner, the new 4P’s of data-driven marketing are Purpose, People, Process, Platform. Only when is defined for what Purpose data is processed, People can define Processes, thereby making best use of the Smart Data. Then they can establish the appropriate IT equipment (Platform), thus achieving an optimum yield of Smart Data across all processing steps.
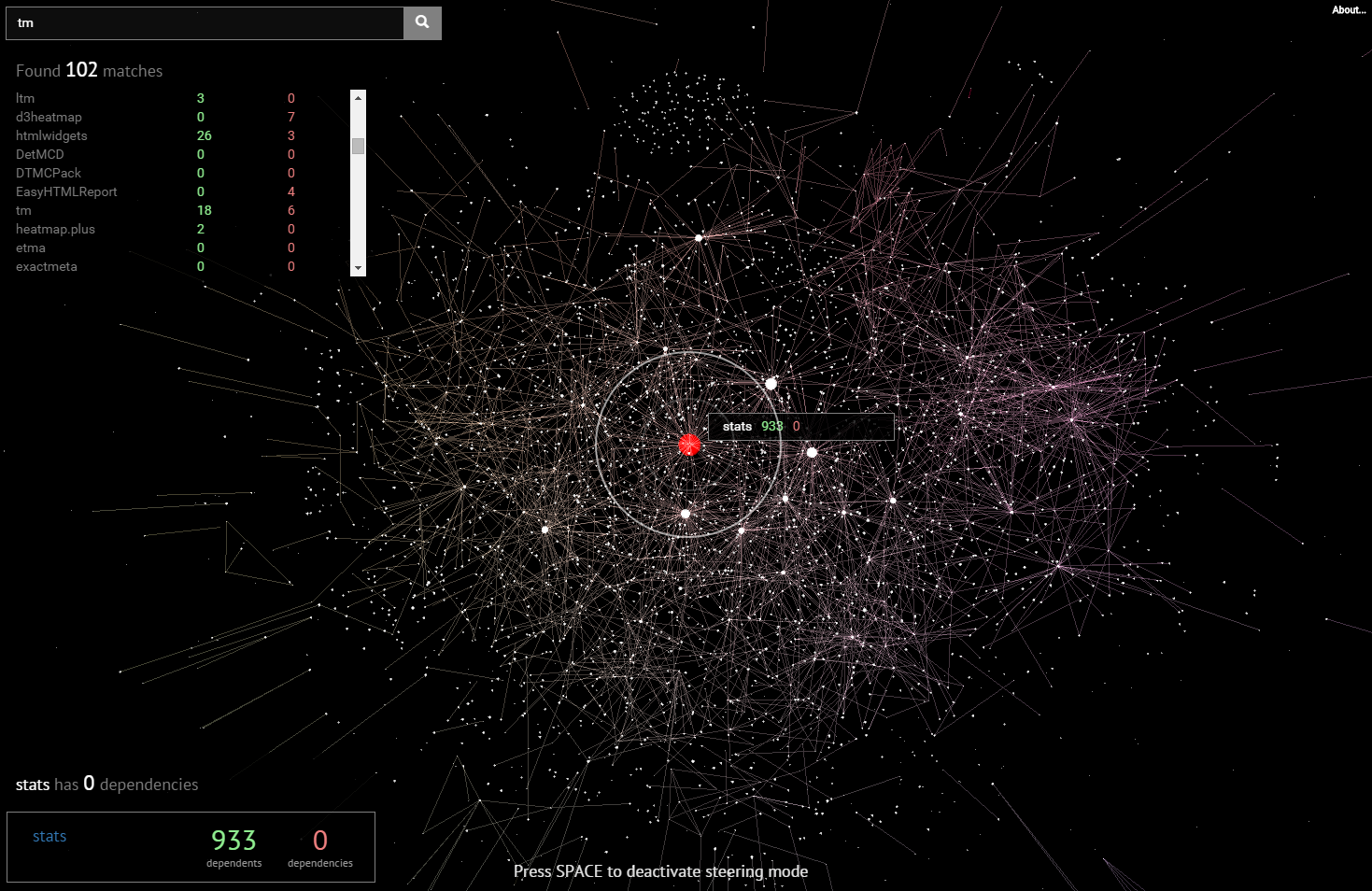
Software Galaxies: 3D CRAN Network Graph - R Language
 BeMined
BeMined